Do you know?
Over billions of people in world consuming skin whitening tablets does not know how much glutathione to take for skin whitening?
In recent years, skin whitening and lightening have been a major fascination in many parts of the world. Skin color is believed to be a symbol of social prestige and appearance. But it is also worth considering whether our fascination with skin whitening is driving us to invest blindly in the fake, toxic cosmetic sector.
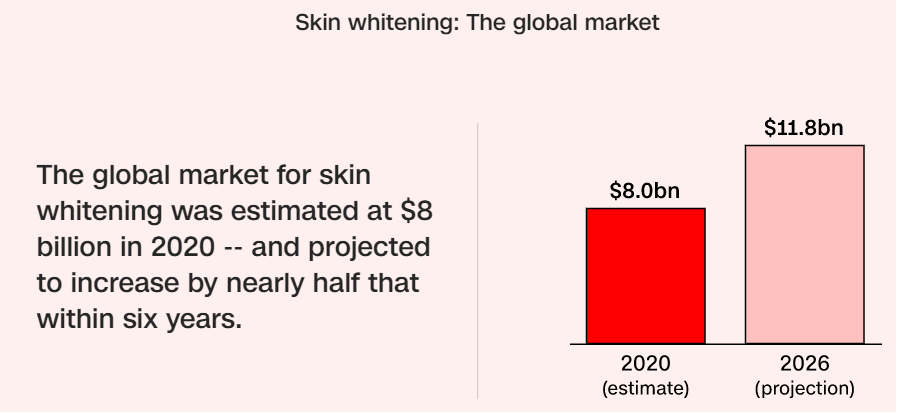
“The global marketplace for skin whitening is anticipated to grow to 11 billion dollars by 2027, up from 8 billion dollars in 2020.” consistent with the research conducted by CNN’s equal editions.
People become insecure as a result of their obsession and deep-rooted inclination toward colorism for better jobs, marriages, and social status prospects. Another astonishing fact researched by CNN is that “women account for 80% of worldwide sales.”
The huge off-beam investment in creams has been estimated to reach $8 billion by 2027. For the sake of growing business, many manufacturing industries would hardly inform you what could happen if one consumes Glutathione pills for a prolonged period of time.
This article emphasizes the role of glutathione for skin and body, how much glutathione to take for skin whitening, and its associated risk factors.
The focus of this post will be on several organic ways to take glutathione and its primary health benefits for better body functioning in old age.
What is Glutathione?
Glutathione is a strong, active antioxidant molecule made up of three amino acids produced by the body. The main function of glutathione is to ensure the overall well-being of the body. It works in tissue building and repair to maintain the immune system, protecting the body from free radicals and saving crucial body cells.
The other external factors that affect glutathione levels in the body are:
- Toxins in the environment
- Prolonged sunlight exposure
- Negative stress
Skin whitening
Glutathione-How it works
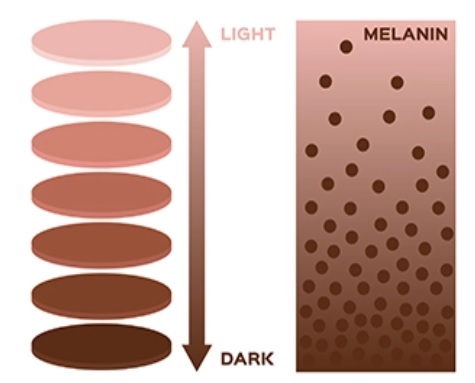
Melanogenesis increases with more exposure to UV radiation. The external application of glutathione for skin whitening after exposure to UV radiation blocks the free radical oxygen species formed in epidermal cells in the outer layer of skin. These free radicals are responsible for wrinkles, blemishes, and skin aging.
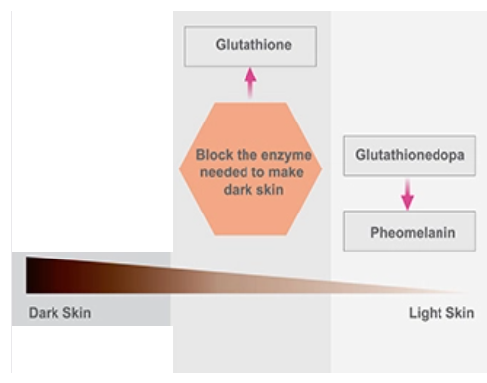
How much glutathione to take for skin whitening ?
Glutathione Dosage for Skin Whitening
There are specific questions that float in every individual’s mind who has started their skin whitening glutathione dosage.
How long does it take glutathione to lighten skin?
Then there are certain points you need to know about the glutathione based cosmetic industry. After learning that glutathione impacts skin whitening and lightening, manufacturers saturated the market with commercial glutathione topical products, including creams, lotions, and face washes, claiming that they perform effectively on patchy skin. It has been observed that there is a significant effect on the skin tone of certain age groups of women. It is seen in definite exposed and unexposed areas of their bodies, like the right and left areas of their faces and the inner and outer forearms.
Since there is no standardized dosage decided yet by the food and drug administration department of any country, the dosage has been set solely by pharmaceutical manufacturers. The enticing offers and over-the-counter availability of skin whitening drugs attract customers to buy and consume improper dosages.
According to different manufacturers in oral therapy, the recommended glutathione dosage for skin lightening in glutathione tablets is 20–40 mg/kg body weight per day in two doses. For the visibility of skin lightening effects, a dosage of 500mg per day for an indefinite time has been suggested. It takes, on average, 4-6 months to witness a skin-lightening effect on the skin. Studies have claimed that on discontinuing the glutathione dosage, the normal skin complexion will return to its original form. Although the safety profile of creams, lotions, and oral glutathione is reasonably safe.
With the scarcity of oral glutathione dosage for skin in the market, intravenous glutathione injections were promoted to provide an instantaneous skin lightening impact. The manufacturers recommended 600–1200 mg once or twice weekly, but surprisingly, there is no clinical trial that has been tested as of yet.
But in an unpublished observation, the practitioners revealed on the basis of trails that the patchy hypopigmentation tended to resolve after 30–40 doses of glutathione injections. There is insufficient research information to prove the correct glutathione dosage.
www.fda.gov.ph
Best Glutathione Supplement for skin whitening
Glutathione Natural sources and supplements
Glutathione in dietary and supplement form is considered harmless by the federal food, drug, and cosmetics food and drug administration in the U.S. The best glutathione supplement is available online and in the market of India, Japan, and the Philippines.
The glutathione supplements available on the market are
Vitamin E
Selenium
Curcumin
Even if these are the best glutathione supplement benefits are natural, it is best to see your doctor before taking them.
Glutathione rich foods
Our body does not absorb glutathione directly from foods. However, certain foods that are abundant in sulfur-containing amino acids that are found in glutathione can help boost glutathione levels in the body.
- Broccoli
- Unprocessed meat
- Turkey
- Yogurt
- sunflower seeds
- Asparagus
- Garlic
- Walnut
- Legumes
- Eggs
- lentils
- Spinach
- Avocados
Certain herbs that help naturally raise glutathione levels in the body are milk thistle, beetroot, flax seeds, whey, etc.
Glutathione benefits
- Improvement of alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD)
- Weight management and insulin resistance.
Glutathione helps with fat burning in old people because as they age, their bodies produce less glutathione and they gain weight. Therefore, fat burning leads to insulin resistance. Adding supplements like cysteine and glycine increases glutathione levels in just 2 weeks, leading to fat loss and insulin resistance.
- Improvement of Parkinson’s disease (PD)
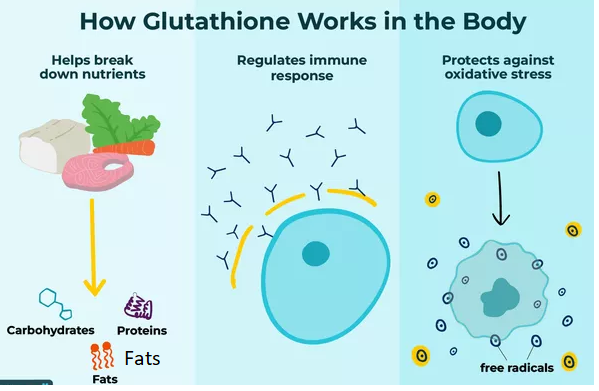
According to the latest research in 2021, it has been proposed that Parkinson’s disease will increase from 8.7 to 9.3 billion by 2030. It is the second most common neurodegenerative disease in the world. One of the most important benefits of glutathione is that it can help reduce oxidative stress by neutralizing reactive oxygen species, thus protecting against oxidative stress.
Conclusion
Glutathione is a natural amino acid produced by our body. But, due to its active antioxidant property, it fights against many rare medical conditions thus increasing the quality of life.
Instead, focusing on work and promoting messages to inhibit insecurities about skin color among people, The cosmetic market in certain countries is using toxic components in beauty products, causing life-threatening diseases. Third-party sites, many social media channels, and MNCs are still continuing the production and use of glutathione even knowing that it may have an adverse impact on individuals’ health.
Sources
- Skin whitening: What is it, what are the risks, and who profits?
By Meera Senthilingam, Pallabi Munsi and Vanessa Offiong, CNN
- Glutathione as a skin whitening agent: Facts, myths, evidence and controversies
https://ijdvl.com/glutathione-as-a-skin-whitening-agent-facts-myths-evidence-and-controversies/
- Glutathione for skin lightening: a regnant myth or evidence-based verity?
Sidharth Sonthalia, corresponding author1 Abhijeet K. Jha,2 Aimilios Lallas,3 Geraldine Jain,4 and Deepak Jakhar5 Published online 2018 Jan 31. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0801a04
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5808366/


